If you are like me, understanding cryptocurrency is confusing. I need to have a blockchain simplified to understand why you would want to get into cryptocurrency. For instance, terminologies such as blockchain, hash nodes, proof of work might as well be a foreign language.
Block Chain Made Simple
From my understanding, the Blockchain is the backbone of cryptocurrency. With that in mind, the information that follows should help to understand the blockchain function involved in cryptocurrency.
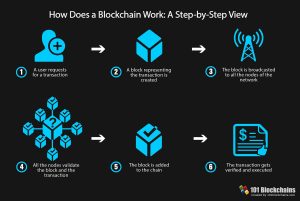
Blockchain simplified is defined as a group of digital information (block) that is stored in a public database (chain). A single block on a Bitcoin BlockChain holds up to 1 MB of data. Depending on the transaction size, a block can hold a few thousand transactions. The Blocks on a blockchain consist of digital bits of information in three parts.
- First, block stores information on transactions such as dates, time and $$ amounts
- Second, Block stores information about who was involved in the transaction. But the information is recorded without any identifying information. Instead, Block uses a unique digital signature line such as a username.
- Third, the information stored is distinguished from other blocks by a unique code. This unique code is called a hash.
Block Chain Simplified – Security
So you may be asking if you can view all transactions then how private is blockchain? Especially, when users can also connect their computers to the blockchain network as Nodes. Therefore, their computers receive a copy of the blockchain. In addition, their computer is updated whenever a new block is added. As such, it acts much like a Facebook News Feed that gives a live update whenever a new status is posted.
Once a block is added to the blockchain, the public can view the transactions including you! If you view a Bitcoin blockchain, you will see the transaction data, along with the information about when (Time), where (Height) and by who (relayed by)o the block was added. The key thing to take away from this is, that no one has access to identify information about the users making transaction. Personal information about the users is limited to their digital signature or user name.
How Secure is Block Chain?
Blockchain technology accounts for security in several ways.  For instance, each new block is always added to the end of the blockchain. Thus, with Bitcoin, you’ll see each block has a position on the chain called a height. As of January 2020, the block’s height exceeded 615,400.
For instance, each new block is always added to the end of the blockchain. Thus, with Bitcoin, you’ll see each block has a position on the chain called a height. As of January 2020, the block’s height exceeded 615,400.
Once a block has been added to the blockchain, it’s difficult to go back and change the contents of the block. This is due to each block has its hash along with the hash of the block before it. With that in mind, hash codes are created by a mathematical function. This mathematical function turns digital information into a string of numbers and letters. Should that information be edited in any way, the hash codes change as well!
Thus, a hacker has to change every single block after it on the blockchain. This requires recalculation of all those hashes along with the need to have an enormous and improbable amount of computing power. As a result, once a block is added to the blockchain, it’s extremely difficult to edit and impossible to delete.
Blockchain Trust Simplified
As a way to address trust issues, blockchain networks require tests for computers to join and add blocks to the chain. These tests are called consensus models. It requires users to “prove” themselves before they can participate in a blockchain network.
The most common test used by Bitcoin is Proof of Work system. Here, a computer has to prove they have done work by solving a complex computational math problem. If the computer comes up with an acceptable solution, that computer then adds the block to the blockchain. This process is called “mining”.
Mining is not an easy process. For example, the odds of solving one of these problems on the Bitcoin Network is about 1 in 15.5 trillion in January 2020. To solve the complex math problems., computers run programs that consume vast amounts of power and energy
Proof of Work doesn’t make attacks by hackers impossible but it doesn’t make it very practical. A hacker would have to take control of more than 51% of all computing power that is on the blockchain. That level of computing power is needed to overwhelm all other participants in the network. To give you a feel for how much power might be required, imagine the electrical power usage of the country of Denmark for a year to achieve the 51% power need.
Origin of Block Chain Technology
Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two researchers, wanted to develop a system whose document timestamps could not be altered. It wasn’t until almost 20 years later with the launch of Bitcoin ins 2009, that the blockchain had its first real-world application
So How Does Bitcoin Work
Probably, there are millions of people around the globe that own at least a portion of bitcoin. So how do you pay to buy goods with bitcoin? This is where blockchain comes into play.
When one person pays another for goods using bitcoins, computers on the Bitcoin network race to verify the transaction. In order to verify the transaction, users run a program on their computer to solve a complex mathematical problem called a hash. When the computer solves the problem by “hashing” a block, it’s an algorithmic work that will also verify the block’s transactions. Once the mathematical problem is solved, the completed transaction is publicly recorded and stored as a block on the blockchain. Plus, at this point the transaction becomes unalterable. The computers that successfully verify blocks are rewarded for their labor with the cryptocurrency. This process is commonly referred to as mining.
Block Chain Simplified – Importance of Wallet
In order to conduct a transaction on the Bitcoin network, participants must  run a program called a wallet. Each wallet consists of two unique cryptographic keys: a public and private key.
run a program called a wallet. Each wallet consists of two unique cryptographic keys: a public and private key.
The public key is the location where transactions are deposited to and withdrawn from. This is also the key that appears on the blockchain ledger as the user’s digital signature. Any payments received in bitcoins to their keys in order to authorize a transaction, you enter with your private key which proves ownership of the funds stored in your wallet address. You need to keep your private key secret, not to share it with anyone. Your private key has a different string of digits than your wallet address. Remember the person that controls the private key owns the funds in a wallet address. So if someone steals your private key, there is so way to prove the coins are yours.
- The public key is created from the private key and is used to create the wallet address. This is the key used in the digital signature of a transaction. This allows the network to verify that the private key was used to sign that transaction. By operating this way, the private key is not revealed when the transaction is broadcasted to the network.
Key Things to Keep in Mind
- Your wallet address needs to be public so that you receive funds from anyone.
- Keep your private key secret; back it up in several secure locations. With that in mind, we do not recommend saving it on your PC.
- Remember Your Private Keys=Your Bitcoin
Hopefully, this bit of information helped explain the complexities of BlockChain and the importance of the Wallet; public, and private. Should you be interested in mining Bitcoin, check out this site
As a follow on an article on BlockChain Simplified, soon to come is a read on the cryptocurrency transaction process. Look for it here soon.